What RAP is
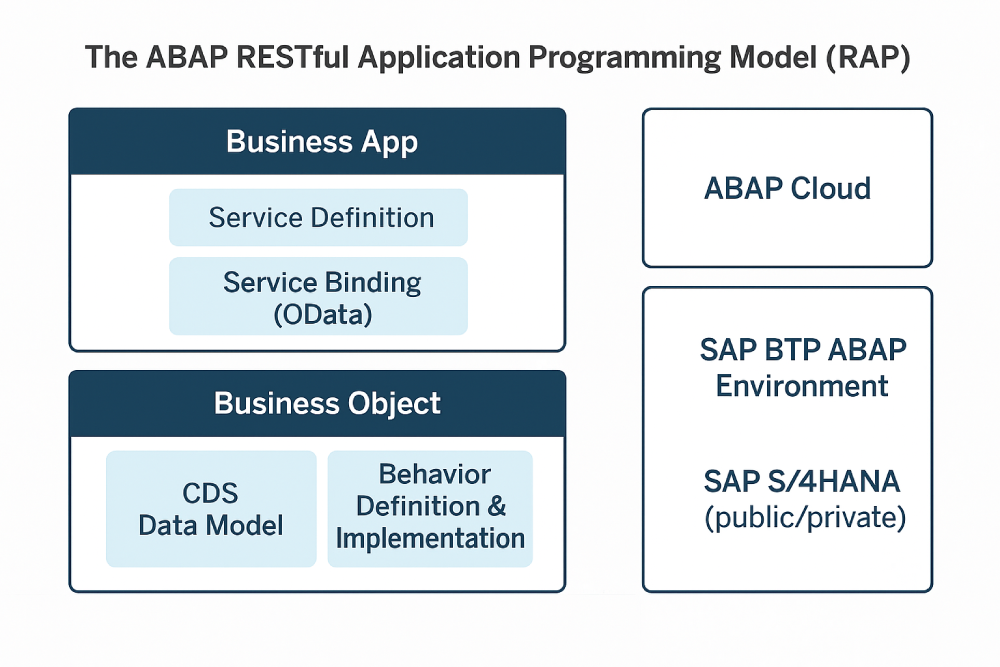
The ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP) is SAP’s end-to-end framework for building cloud-ready, transactional business apps and OData services on ABAP—across SAP BTP ABAP environment and SAP S/4HANA (public/private). It structures development around CDS data models, behavior definitions/implementations (business object logic), and service definition/bindings (typically OData V4), aligning to ABAP Cloud “clean core” principles. SAP Help Portalpages.community.sap.comSAP
Why teams choose RAP
RAP streamlines CRUD, validations, determinations, authorizations, draft handling, and late numbering, so you ship Fiori-ready services without scattering business rules across UI or database layers. When you need to act on business objects programmatically—workflows, background jobs, integration—the Entity Manipulation Language (EML) gives typed, transactional access to BOs while honoring the same rules your UI does. SAP Help Portal+1
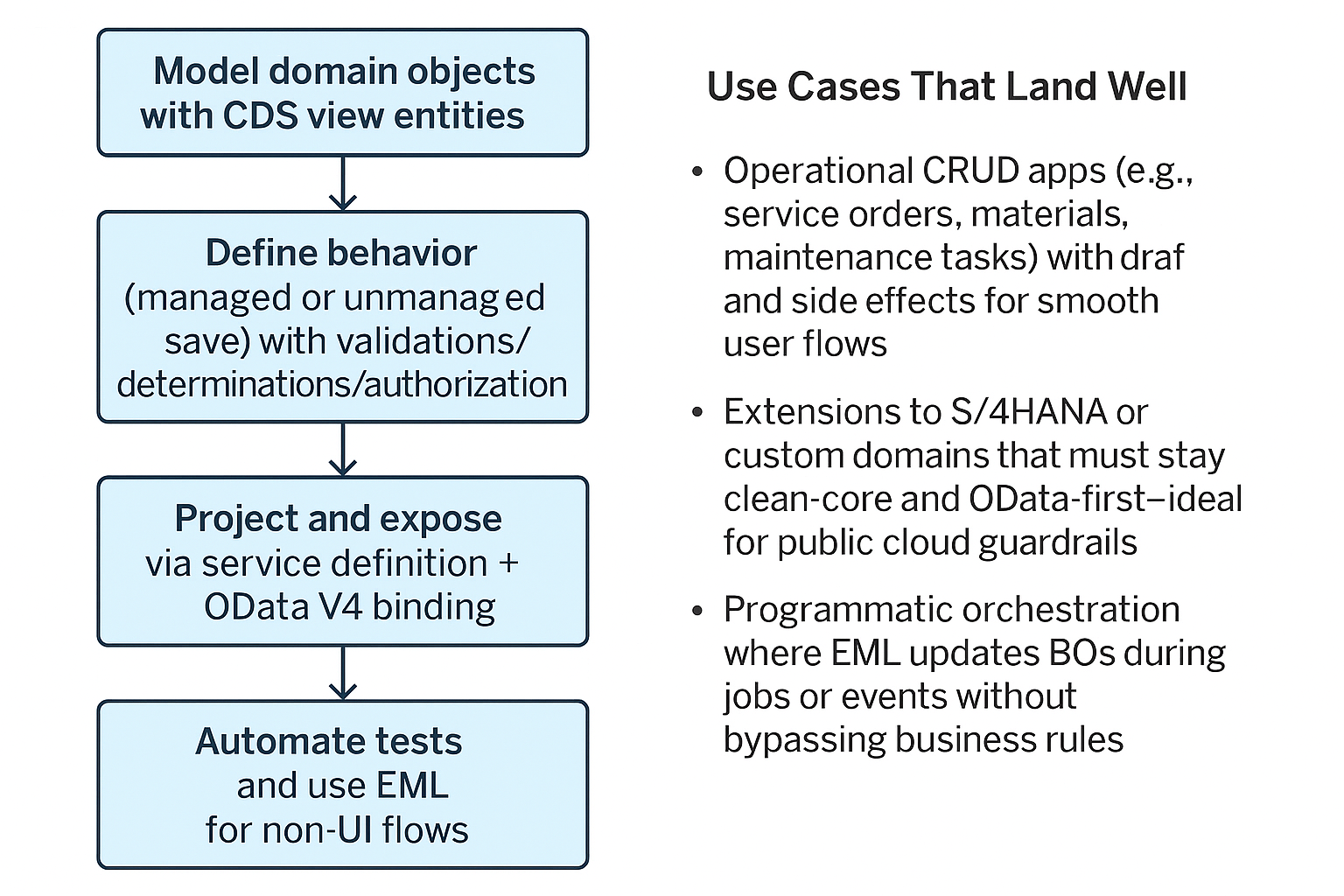
Core building blocks (quick path to first service)
- Model domain objects with CDS view entities; 2) define behavior (managed or unmanaged save) with validations/determinations/authorizations; 3) project and expose via service definition + OData V4 binding; 4) consume with SAP Fiori elements or APIs; 5) automate tests and use EML for non-UI flows. SAP’s “Learn RAP” track and official overview walk these steps in detail. SAP Help Portal+1
Use cases that land well
- Operational CRUD apps (e.g., service orders, materials, maintenance tasks) with draft and side effects for smooth user flows. SAP publishes sample RAP apps (e.g., maintenance-operations products) you can adapt. GitHub
- Extensions to S/4HANA or custom domains that must stay clean-core and O Data-first—ideal for public cloud guardrails. SAP
- Programmatic orchestration where EML updates BOs during jobs or events without bypassing business rules. SAP Help Portal
Do’s (field-tested)
- Prefer managed BOs for most enterprise CRUD; let RAP handle persistence and focus your code on business rules. Use unmanaged save only when legacy or exotic persistence demands it. SAP Community
- Embrace draft & side effects to support multi-step edits, long transactions, and responsive UX; lots of guidance exists for enabling draft correctly. SAP Community+1
- Use EML—not direct SQL—for writes inside ABAP logic so validations/authorizations remain consistent and transactional. SAP Help Portal
- Lean on generators & samples to accelerate scaffolding (entities, behaviors, bindings) and learn idioms the “SAP way” (RAP Generator; RAP workshops). GitHub+1SAP Community
- Keep it clean-core: isolate extensions, follow ABAP Cloud checks, and expose OData V4 services with proper capabilities/annotations and IAM roles. SAP
Don’ts (common pitfalls)
- Don’t bypass the BO with ad-hoc table updates; you’ll break transactional buffers, locks, and determinations. Use behavior implementations/EML. SAP Help Portal
- Don’t mix managed/unmanaged carelessly; unmanaged save inside managed scenarios requires clear boundaries and reasons. SAP Community
- Don’t ship without draft/concurrency strategy; failing to enable draft or to handle save sequences leads to data loss or stale conflicts. SAP Community
- Don’t entangle UI logic with domain rules; keep UI in Fiori elements and put rules inside behavior implementations and CDS annotations. SAP Help Portal

Governance & quality guardrail
Adopt the RAP way of authorizations/validations/determinations, align with ABAP Cloud checks, and version your service contracts. Use the official help guides and SAPinsider’s explainer for architecture walkthroughs and team onboarding. SAP Help PortalSAPinsider








